Algebraic products
This is defined by (4.10) in Section 4.6.
It is denoted by: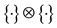 . It is a composite but not explored in any greater detail in this paper.
. It is a composite but not explored in any greater detail in this paper.
Alleles
Similar to chemistry, different configurations of the same sequence.
Alleles in Convolution Range
In complex synthetic sequences of natural numbers, alleles are in two ranges: in the Convolution Range(CR) and Regeneration Ranges (RR). Alleles in CR are outcomes of convolution products and are encapsulated and directly related to the encapsulated generation of the parent sequence. They are denoted as:
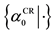
where  denotes allele, its superfix CR signifies convolution range.
denotes allele, its superfix CR signifies convolution range.
Alleles in Regeneration Range
In complex synthetic sequences of natural numbers, alleles are in two ranges: in the Convolution Range(CR) and Regeneration Ranges (RR). Alleles in RR are outcomes of direct products and are encapsulated and directly related to the encapsulated degree of the parent sequence. They are denoted
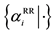
where 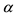 denotes allele, its superfix RR signifies the range and the suffix i signifies its allele position.
denotes allele, its superfix RR signifies the range and the suffix i signifies its allele position.
Note that, these alleles are in the regenerating zone and their interoperability operations are rather complicated.
Arithmetic calculus
A term proposed to suggest a systematic approach to summing a family of sequences based on natural numbers.
Base
In combinatoric operators, the base refers to the smaller finite and distinct objects selection from larger ones (which is referred to as the level).
Building blocks
Another term for kernel.
Complexity
The core of a sequence when it is reduced to its rock bottom, related to kernel.
Complexity gain
The kernel of the sequence of natural numbers: 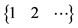 is
is 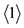 and therefore its complexity by definition is 1. Any other synthetic sequence of natural numbers with a greater complexity has a gain = its complexity size − 1
and therefore its complexity by definition is 1. Any other synthetic sequence of natural numbers with a greater complexity has a gain = its complexity size − 1
Conducement
The operation of systematically summing the terms of a sequence together.
The term is proposed in lieu of summing or integration.
Different notations are used for conducement:
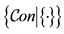 or
or 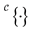 or
or 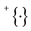
Conducemental
This is a mathematical expression, which expresses the sum. For instance:
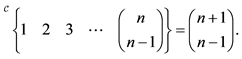
Its conducemental is: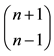 . A conducemental is easily obtained.
. A conducemental is easily obtained.
Conducemental direction
In the Difference table, this is the direction along which.
Convolution products
This is defined by (4.6) in Section 4.4.
It is denoted by: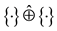 . The accent on
. The accent on  signifies that the products are finite and dipping.
signifies that the products are finite and dipping.
Degree
The degree of a sequence is directly related to the effect of using the direct product rule. Some of the rules are presented in heuristic rules terms. It is an important dimension of arithmetic calculus.
Difference Table
This age old method is given a new lease of life when the sequence of counters is superimposed on its diagonals. This paper show in Section 7 that the Difference Table has many generic zones and offers appropriate terms to describe them.