Method
Advantages
Disadvantages
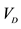
Easy to quantify as inputs known
Only at specific time, small error in P
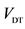
Solid input for some products, future extrapolation has low error
Demands future extrapolation and resultant errors for all inputs
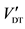
Provides total value with low error
Demands future extrapolation, difficult quantification of secondary benefits

Easy calculated precise value for single company
Only useful for single company
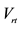
ND available and generalized cost assumptions tolerable
Uses P and associated errors, assumes all firms have similar costs and values, demands future extrapolation
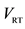
Captures value throughout time
P errors, Firm value/costs errors, demands future extrapolation
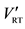
Captures total value with solid foundation for direct costs
P errors, Firm value/costs errors, Demands future extrapolation, quantification of secondary benefits difficult
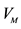
Easy to calculate
Only true if mass-scale distributed manufacturing established at single time, misses all secondary benefits

Relatively easy to calculate
Only valid if mass-scale distributed manufacturing established, demands future extrapolation and resultant errors

Approaching the optimal deployment and thus value of OSH
Only valid if mass-scale distributed manufacturing established, demands future extrapolation, estimation of secondary benefits and resultant errors