Policy
Brief description
Advantages
Disadvantages
LRU
The least recently used objects are removed first.
Simple and efficient with uniform size objects, such as the memory cache.
Ignores download latency and the size of Web objects
LFU
The least frequently used objects are removed first.
Simplicity
Ignores download latency and size of objects and may store obsolete Web objects indefinitely.
LFU-DA
Dynamic aging factor (L) is incorporated into LFU.
§ Reduces cache pollution caused by LFU.
§ High byte hit ratio
May suffer from hit ratio
SIZE
Big objects are removed first
Prefers keeping small Web objects in the cache, causing high cachet hit ratio.
§ Stores small Web objects even if these object are never accessed again.
§ Low byte hit ratio.
GDS
It assigns a key value to each cached object g as equation below. The object with the lowest key value is replaced first.
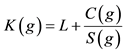
where C(g) is the cost of fetching g from the server; S(g) is the size of g; and L is an aging factor.
§ Overcomes the weakness of SIZE policy by removing objects which are no longer requested by users.
§ High hit ratio
§ Does not take into account the previous frequency of Web objects.
§ Low byte hit ratio.
GDSF
It extends GDS by integrating the frequency factor into the key value
§ Takes into account the previous frequency of Web objects.
§ Very high hit ratio
§ Does not take into account the predicted accesses
§ Low byte hit ratio.