Presence of any of the Following Features makes ICU Admission Obligatory
c ICU admission for CVP monitoring is recommended in patients with history of significant cardiac or renal impairment/or with persistent oliguria or anuria*.
c Altered level of consciousness
c Respiratory rate > 35/min
c Refractory hypotension
c Need for mechanical ventilation
c Plasma osmolality is >320
c pH at 7.0 or below
c Hypokalemia at the time of presentation
ü Identify the precipitant for the acute attack:
New diagnosis of DM c Acute infection c Lack of medications
c Poor compliance to treatment c Acute stress (CVA, ACS etc.) c Pregnancy
c Exposure to Meds c Other (specify)
DKA Immediate Management: Treatment of DKA includes administration of intravenous fluid to correct dehydration and hyperosmolarity, administration of insulin to reverse hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis, correction of electrolyte abnormalities, identification of precipitants, and frequent patient monitoring. Complications of treatment include hypoglycemia; hypokalemia; and rarely, cerebral edema.
IV Fluid and Insulin Infusion Switch: Criteria for switch include: patient is fully conscious, able to take orally, first sc insulin dose given one to two hours earlier, 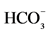 > 18 mmol/l, anion gap < 14 and pH > 7.3. Start with patient’s usual insulin regimen, adjusted if need be. New patient: Sc insulin at a total daily dose of 0.7 unit/kg divided as follow: −2/3 for am dose (1/3 R & 2/3 NPH), −1/3 for pm dose (1/2 R & 1/2 NPH)
> 18 mmol/l, anion gap < 14 and pH > 7.3. Start with patient’s usual insulin regimen, adjusted if need be. New patient: Sc insulin at a total daily dose of 0.7 unit/kg divided as follow: −2/3 for am dose (1/3 R & 2/3 NPH), −1/3 for pm dose (1/2 R & 1/2 NPH)
Promote self-management plan/Home Blood Glucose Monitoring/ home ketostix for those with frequent DKAs.
Discharge: If the patient has met the above criteria, is established on a reasonably adequate insulin regimen, precipitant of DKA resolved or under control and is seen by the diabetes educator.
Follow-up: in endocrine clinic in 2 - 4 weeks.